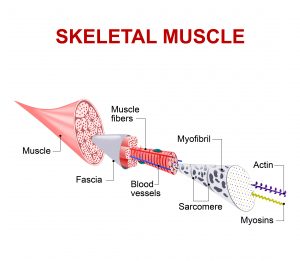
What is contracture?
Following brain injury contractures may develop. Muscle fibres lose the number of contractile units along their length, which results in muscle becoming shortened. Contractures develop as result of muscles being held in a shortened position. Severe spasticity holds the muscle in shortened positions. Therefore severe spasticity often results in the development of contractures.
How does this affect the person?
Muscles become shortened resulting in reduced mobility, poor postures and abnormal limb positioning.
How to Help:
Contractures should be managed in the same way as spasticity to prevent worsening:
- Give affected parts of the body a chance to relax by providing good support to the trunk and limbs affected (Postural Management and Seating).
- When moving a limb or opening a tight hand, use slow supported movements.
- Reduce anxiety by offering reassurance and avoiding surprises by preparing a person for movement with explanations.
Physiotherapists and/or Occupational Therapists may provide strategies (e.g. splints) to manage the contractures.