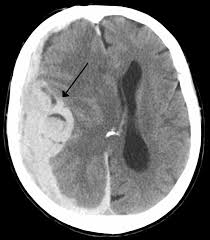
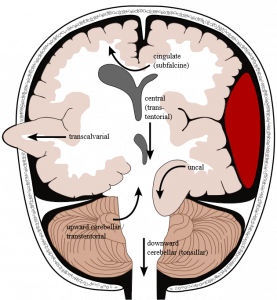
Midline shift refers to a shift (displacement) of brain tissue across the centre line of the brain. It may occur following traumatic brain injury in association with raised intracranial pressure or an intracranial haematoma which can push the brain towards one side causing midline shift. Herniation occurs when parts of the brain are squeezed through structures within the cranium. As the pressure inside the cranium increases, parts of the brain are subject to extreme pressure and this may result in herniation. This can occur in two main ways:
- Brain tissue is herniated (forced) through the thick layer of dura which lies between the cerebrum and the cerebellum (the ‘tentorium cerebelli’). This is called tentorial herniation.
- The cerebellum may be herniated (forced) through the base of the skull (foramen magnum). This is called tonsillar herniation and it is very dangerous as it causes life-threatening pressure on the brainstem.
Midline shift and herniation cause extreme pressure on parts of the brain resulting in the blood supply to various parts of the brain being compromised. This can be fatal and is considered a medical emergency.