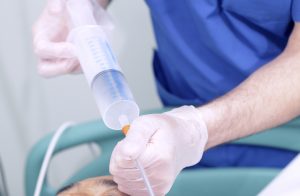
In the context of a patient requiring enteral feeding a suitable individualised feeding regimen will need to be prescribed by the dietitian in liaison with the multidisciplinary team. This nutrition will be administered by an enteral feeding tube. There are two main methods of administration, pump assisted feeding and bolus feeding, both of which may be appropriate at different times in the patient journey.
Continuous (pump-assisted) feeding refers to the provision of nutrition and hydration via the tube using a pump for a continuous period lasting several hours. The benefits of this include:
- It allows patients to be fed over long periods.
- Administration of feed is less time consuming.
- It is associated with reduced complications.
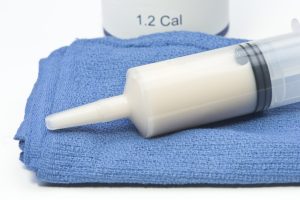 Bolus (syringe) feeding refers to the provision of nutrition and hydration via the tube using a syringe at several intervals throughout the day. The advantages bolus feeding may have over pump assisted feeding include:
Bolus (syringe) feeding refers to the provision of nutrition and hydration via the tube using a syringe at several intervals throughout the day. The advantages bolus feeding may have over pump assisted feeding include:
- Normal meal time patterns can be reproduced i.e. bolus feeds at breakfast, lunch and dinner.
- It allows the patient to have more freedom and less time spent attached to a pump.
- It may be more suited to a rehabilitation environment.
Disadvantages of bolus feeding may include:
- It may require more nursing time.
- It may be associated with gastrointestinal side effects.
Common complications of enteral feeding may include:
 Risk of re-feeding syndrome if the person has not received nutrition for more than 5 days. This refers to a metabolic disturbance occurring when the patient is given nutrition again (electrolyte disturbance potentially leading to neurological, cardiac, respiratory and other possible complications). Careful monitoring is required.
Risk of re-feeding syndrome if the person has not received nutrition for more than 5 days. This refers to a metabolic disturbance occurring when the patient is given nutrition again (electrolyte disturbance potentially leading to neurological, cardiac, respiratory and other possible complications). Careful monitoring is required.- Risk of aspiration (higher risk with nasogastric feeding when compared with other methods of enteral feeding).
- Gastrointestinal disturbances e.g. vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation.
- Tube blockage.
- Stoma site problems (surgical opening through which the tube is inserted).
- Poor oral hygiene and oral discomfort.